노면 기호는 운전자를 안내하고 안전을 보장하며 도로와 고속도로의 질서를 유지하는 데 필수적인 요소입니다. 노면 기호는 안료 에 사용되는 안료는 그 효과에 결정적인 역할을 합니다. 이 글에서는 도로 표지판에 사용되는 다양한 유형의 안료의 특성을 살펴보고 각 유형이 특정 용도에 적합한 이유를 강조합니다. 도로 안전 전문가, 화학 애호가 또는 단순히 호기심이 많은 사람이라면 이 가이드를 통해 노면 표시 안료에 대한 심층적인 이해를 얻을 수 있습니다.
도로 표지판에서 안료의 중요성
안료가 중요한 이유
안료는 단순히 색상을 추가하는 데 그치지 않고 노면 표시의 성능, 내구성 및 가시성에 큰 영향을 미칩니다. 올바른 안료를 선택하면 다양한 조명 조건에서 노면 표시가 잘 보이고 마모에 강하며 열악한 환경 요인에도 견딜 수 있습니다.
도로 표지판에서 안료의 주요 역할
- 가시성: 낮과 밤 모두 노면 표시가 잘 보이도록 합니다.
- 내구성: 교통량과 날씨로 인한 마모를 견딜 수 있도록 마킹을 지원합니다.
- 반사성: 야간 시인성을 높이기 위해 빛을 반사하는 마킹의 기능을 개선합니다.
- 환경 저항: 자외선, 열, 추위, 습기에 대한 내성을 제공합니다.
도로 표시에 사용되는 안료의 종류
노면 표시에 사용되는 안료는 크게 무기 안료와 유기 안료로 분류할 수 있습니다. 각 유형에는 고유한 특성, 장점 및 단점이 있습니다.
1. 무기 안료
무기 안료는 안정성, 내구성, 환경적 요인에 대한 저항성으로 잘 알려져 있습니다. 광물과 금속에서 추출하여 열악한 조건에서도 견고한 성능을 제공합니다.
a. 이산화티타늄(TiO2)
속성:
- 높은 밝기 및 불투명도: 이산화티타늄은 눈부신 화이트닝과 뛰어난 커버력을 제공합니다.
- 자외선 저항: 자외선에 대한 내성이 뛰어나 변색과 품질 저하를 방지합니다.
- 무독성 및 환경 친화적입니다: 이산화티타늄은 노면 표시에 사용하기에 안전합니다.
애플리케이션:
- 흰색 노면 표시에 널리 사용됩니다.
- 마킹의 가시성과 수명을 향상시킵니다.
b. 산화철
속성:
- 다양한 색상: 빨간색, 노란색, 갈색, 검은색으로 제공됩니다.
- 높은 불투명도 및 착색 강도: 산화철은 강력한 색상과 뛰어난 커버력을 제공합니다.
- 자외선 및 내후성: 이 안료는 열악한 환경 조건에서도 견딜 수 있습니다.
애플리케이션:
- 컬러 도로 표시(예: 자전거 도로, 횡단보도)에 사용됩니다.
- 오래 지속되는 색상 유지력을 제공합니다.
c. 산화 크롬 녹색
속성:
- 딥 그린 색상: 크롬 산화물 녹색은 풍부하고 안정적인 녹색 색조를 제공합니다.
- 내광성 및 내후성: 빛과 날씨에 장시간 노출되어도 색상이 유지됩니다.
- 내화학성: 다양한 화학 물질에 대한 내성이 있어 수명이 길어집니다.
애플리케이션:
- 녹색 도로 표시(예: 버스 차선, 자전거 도로)에 사용됩니다.
- 실외 환경에서도 내구성을 보장합니다.
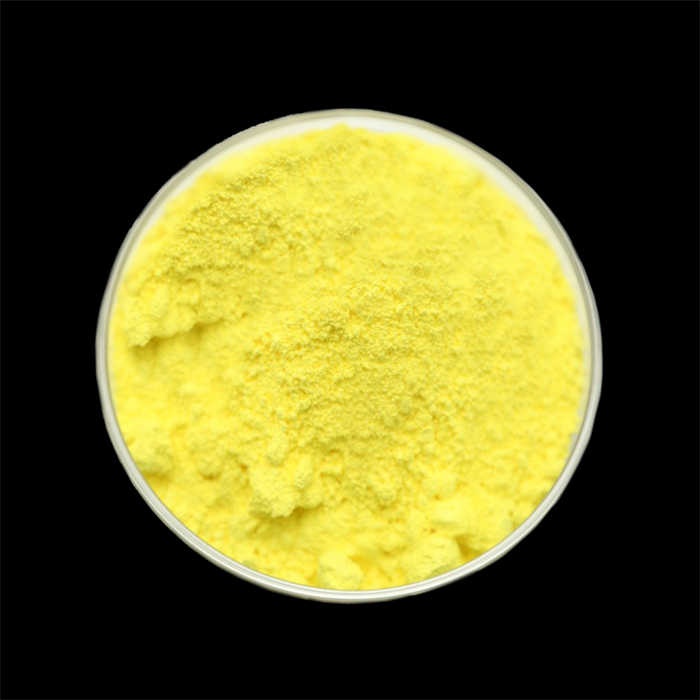
d. 납 크롬산염
속성:
- 밝은 노란색과 주황색: 납 크롬산염은 높은 가시성과 함께 생생한 색상을 제공합니다.
- 높은 불투명도 및 색상 강도: 뛰어난 커버력과 강력한 색상을 제공합니다.
- 날씨 및 자외선 차단: 이 색소는 내구성이 뛰어나지만 독성 문제로 인해 선호도가 떨어졌습니다.
애플리케이션:
- 역사적으로 노란색 도로 표시에 사용되었습니다.
- 현재는 건강과 환경에 대한 우려로 인해 대부분 더 안전한 대체품으로 대체되었습니다.
2. 유기농 안료
유기 안료는 탄소 기반이며 생생한 색상을 제공하지만 일반적으로 무기 안료에 비해 안정성이 낮습니다. 기술의 발전으로 성능이 향상되어 다양한 용도에 적합합니다.
a. 프탈로시아닌 블루 및 그린
속성:
- 생생한 색상: 프탈로시아닌 색소는 밝은 파란색과 녹색 색조를 제공합니다.
- 내광성 및 내후성: 빛과 날씨에 노출되어도 색상을 유지합니다.
- 높은 착색 강도: 이 색소는 소량으로도 강력하고 효과적입니다.
애플리케이션:
- 파란색 및 녹색 도로 표시에 사용됩니다.
- 장식 및 안전 목적에 적합합니다.
b. 퀴나크리돈 색소
속성:
- 색상 범위: 빨간색, 주황색, 보라색 색상으로 제공됩니다.
- 내광성 및 내후성: 퀴나크리돈 안료는 내구성이 뛰어나고 색이 바래지 않습니다.
- 색상 강도 및 투명도: 강렬하고 투명한 색상을 제공합니다.
애플리케이션:
- 컬러 도로 표시에 사용됩니다.
- 오래 지속되고 선명한 색상을 제공합니다.
무기 안료와 유기 안료 비교하기
| 측면 | 무기 안료 | 유기농 안료 |
|---|---|---|
| 색상 범위 | 제한적이지만 안정적인 색상 | 다양하고 생생한 색상 |
| 내구성 | 높은 내구성과 안정성 | 내구성은 향상되었지만 일반적으로 낮은 |
| 환경 저항 | 뛰어난 자외선 및 내후성 | 발전과 함께 우수한 저항력 |
| 불투명도 | 높은 불투명도 및 밝기 | 착색 강도는 높지만 불투명도가 낮을 수 있습니다. |
| 독성 | 일반적으로 낮은 독성(크롬산염 납 제외) | 낮은 독성 |
| 비용 | 일반적으로 미네랄 추출로 인해 더 높습니다. | 합성 제작으로 비용 효율적일 수 있습니다. |